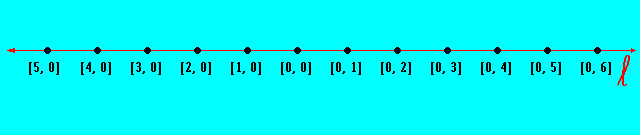Where: a - n must be a whole number. Subtraction only
works if n is less than or equal to a.
In other words: a - n and b - n must be
just those subtractions that are closed
operations in the set of whole numbers.
5 - 7 is not possible since 7 is greater than 5.
5 - 7 is not a closed operation in W.
Examples: [0, 0] = [1, 1] = [3, 3] = ... = [5280, 5280] = . . . ,
[1, 3] = [5, 7] = [51, 53] = ... = [a, a + 2] = . . .
Properties: The Reflexive, Symmetric, Transitive and
Substitution properties hold in E.
SIMPLE: [a, b] is simple when a = 0 or b = 0 or both
for whole numbers a and b.
Examle: [0, 3] is simple and [14, 17] is not.
Simplify: [0, 3] is a simplified [50, 53].
ADDITION: [a, b] + [c, d] = [a + c, b + d]
for whole numbers a, b, c and d.
Where: a + c and b + d are whole number additions.
Example: [1, 5] + [7, 4] = [1 + 7, 5 + 4] = [8, 9]
also: [1, 5] + [7, 4] = [8, 9] = [0, 1] when simplified.
SUBTRACTION: [a, b] - [c, d] = [a, b] + [d, c]
for whole numbers a, b, c and d.
Where: a + d and b + c are whole number additions.
Example: [1, 5] - [7, 4] = [1, 5] + [4, 7] = [5, 12]
also: [1, 5] - [7, 4] = [0, 7] when simplified.
MULTIPLICATION: [a, b] [c, d] = [ad + bc, ac + bd]
for whole numbers a, b, c and d.
Where: ac + bd are whole number operations and
ad + bc are whole number operations.
Example: [1, 5] [7, 4] = [4 + 35, 7 + 20] = [39, 27]
also: [1, 5] [7, 4] = [12, 0] when simplified.
DIVISION: Division is not a closed operation on set E.
Simplify numbers first to [y, 0], [0, y], [x, 0] or [0, x] ε E.
DIVISION: Assume x is not 0 and y = xk, for k ε W, then:
[y, 0]/[x, 0] = [0, k],
[y, 0]/[0, x] = [k, 0],
[0, y]/[x, 0] = [k, 0] or
[0, y]/[0, x] = [0, k] or
Where: x|y is the whole number relation: x divides y.
Examples: [0, 4]/[0, 2] = [0,2], [9, 0]/[0, 3] = [3, 0]
[8, 0]/[4, 0] = [0, 2], [0, 7]/[7, 0] = [1, 0]
SEQUENCE LINE: Each [a, b] ∈ E is a point along an infinite straight line.
SEQUENCE LINE : Each [a + 1, b] ∈ E is a point one unit to the left of [a, b]
SEQUENCE LINE DIRECTION: Each [a, b + 1] ∈ E is a point one unit to the right of [a, b]
SEQUENCE LINE: All [a, b] ∈ E form an infinite sequence of points that lie on a line but the line is not included with the points. The SEQUENCE LINE, L, is the geometry of just points [a, b] ∈ E for each a ∈ W and b ∈ W.
GRAPH 1.